Understanding Neurofeedback: Equipment, Training, and Professional Development
Neurofeedback is a cutting-edge technique used to train the brain to function more effectively, offering promising therapeutic benefits for a variety of conditions, including anxiety, ADHD, insomnia, and PTSD. By utilizing real-time feedback, neurofeedback allows individuals to learn to regulate brainwave activity, leading to improved cognitive function, emotional regulation, and overall well-being. As neurofeedback continues to gain popularity, the demand for trained professionals and the appropriate neurofeedback equipment has grown significantly. This article explores the essentials of neurofeedback, including the equipment used, the training required for technicians, and opportunities for professional development such as APA Continuing Education credits.
What is Neurofeedback?
Neurofeedback, also referred to as EEG biofeedback, is a process that measures brainwave activity and provides feedback to the individual to help them regulate their brainwave patterns. Through this feedback loop, individuals can learn to increase or decrease the amplitude of certain brainwave frequencies to promote optimal brain function. This non-invasive approach has been shown to have positive outcomes for a wide range of mental health and neurological issues.
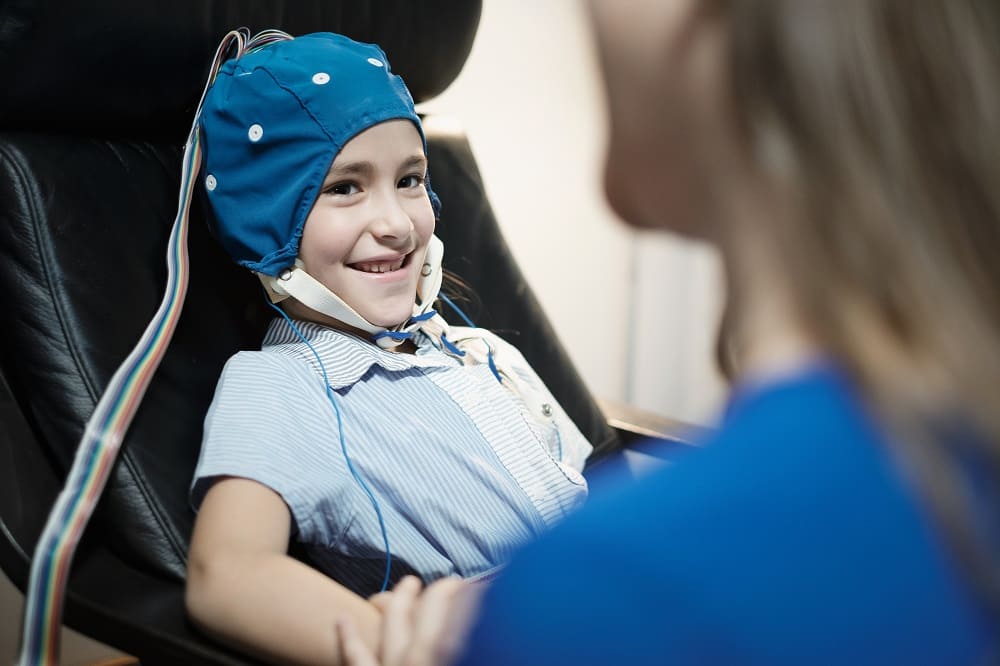
During a neurofeedback session, sensors are placed on the scalp to monitor brainwave activity. The collected data is then sent to a computer system where it is processed and displayed in real-time, often as a visual or auditory cue. For example, the patient might be shown a video game or animation, where the game responds to their brain activity by speeding up or slowing down depending on their brainwave regulation.
The Role of Neurofeedback Equipment
At the core of every neurofeedback session is the neurofeedback equipment, which typically consists of EEG sensors, amplifiers, and software. The EEG sensors are the key components, as they detect electrical activity from the brain and send this data to a computer system for processing.
The quality of neurofeedback equipment plays a critical role in the effectiveness of the treatment. Modern neurofeedback systems feature advanced sensors that ensure accurate readings of brainwave activity, alongside sophisticated software designed to present the feedback in a way that is engaging for the patient. For example, there are different types of neurofeedback equipment suited for various purposes, from basic brain training to more specialized therapeutic uses such as neurotherapy for traumatic brain injuries or mood disorders.
When selecting neurofeedback equipment, it’s essential for practitioners to consider factors such as the number of channels (which corresponds to the number of areas of the brain being monitored), the software’s interface, and the overall usability and reliability of the system.
Neurofeedback Technician Training
Becoming proficient in neurofeedback therapy requires specialized training. A neurofeedback technician is a professional who assists in conducting neurofeedback sessions under the guidance of a licensed therapist or clinician. These technicians must be well-versed in both the theory and practice of neurofeedback, as well as the use of neurofeedback equipment.
To ensure that technicians are properly prepared to offer these services, neurofeedback technician training programs are available through various organizations and educational institutions. These training programs generally cover topics such as the principles of neurofeedback, the types of brainwave patterns, how to set up and calibrate equipment, and how to interpret the data to create effective treatment protocols. Additionally, a well-rounded program will emphasize patient communication, ethical considerations, and ongoing data analysis to track treatment progress.
For those seeking more advanced certification, some programs offer certification through the Biofeedback Certification International Alliance (BCIA), a leading body in biofeedback and neurofeedback certification. This certification helps professionals demonstrate their expertise and commitment to high standards in neurofeedback practice.
Professional Development and APA Continuing Education Credit
Continuing education is an important aspect of any healthcare profession, and neurofeedback is no exception. Professionals seeking to deepen their knowledge and skills in neurofeedback can benefit from APA Continuing Education credit programs. The American Psychological Association (APA) provides accredited continuing education opportunities for psychologists and other mental health professionals. These courses typically include both in-person and online options, allowing practitioners to stay up to date with the latest research, techniques, and developments in the field of neurofeedback.
By earning APA Continuing Education credit, professionals can enhance their understanding of neurofeedback, integrate new approaches into their practice, and stay ahead in an evolving field. These courses are often designed to meet the needs of a diverse audience, including neurofeedback technicians, therapists, psychologists, and other mental health practitioners.
Conclusion
Neurofeedback offers significant potential for improving mental and emotional well-being, and with the growing demand for these services, neurofeedback professionals are crucial in ensuring that patients receive high-quality care. From understanding the importance of neurofeedback equipment to receiving the right training and pursuing continuing education opportunities, professionals in the field can enhance their ability to deliver effective therapy.
Neurofeedback technician training, along with APA Continuing Education credit, provides invaluable resources for practitioners eager to stay at the forefront of neurofeedback therapy. Whether you’re just starting in the field or seeking to expand your expertise, pursuing the right training and professional development opportunities will help ensure you can provide the best care possible for those seeking neurofeedback treatment.